Onboard to the Replicated Platform (Helm CLI Installs Only)
This topic provides Replicated onboarding steps for vendors that support Helm CLI installations only for their application.
For information about how to onboard your application to the Replicated Platform to support installations with Replicated installers and the Helm CLI, see Onboard to the Replicated Platform.
Before You Begin
This section includes guidance and prerequisites to review before you begin onboarding your application.
Best Practices and Recommendations
The following are some best practices and recommendations for successfully onboarding with Replicated:
-
When integrating new Replicated features with an application, make changes in small iterations and test frequently by installing or upgrading the application in a development environment. This will help you to more easily identify issues and troubleshoot. This onboarding workflow will guide you through the process of integrating features in small iterations.
-
Use the Replicated CLI to create and manage your application and releases. Getting familiar with the Replicated CLI will also help later on when integrating Replicated workflows into your CI/CD pipelines.
Getting Help from the Community
The Replicated community site is a forum where Replicated team members and users can post questions and answers related to working with the Replicated Platform. It is designed to help Replicated users troubleshoot and learn more about common tasks involved with distributing, installing, observing, and supporting their application.
Before posting in the community site, use the search to find existing knowledge base articles related to your question. If you are not able to find an existing article that addresses your question, create a new topic or add a reply to an existing topic so that a member of the Replicated community or team can respond.
To get help from and participate in the Replicated community, see https://community.replicated.com/.
Prerequisites
-
Create an account in the Vendor Portal. You can either create a new team or join an existing team. For more information, see Create a Vendor Account.
-
Set up your local workstation with the required toolkit for working with the Replicated Platform. See Set Up Your Local Workstation.
-
Make sure you have access to a Kubernetes cluster for testing your releases. For information about how to create a cluster, see Create a Kubernetes Cluster in Set Up Your Environment.
-
Complete a basic tutorial to create an application with a sample Helm chart and then promote and install releases in a development environment. This helps you get familiar with the process of creating, installing, and updating releases in the Replicated Platform. See Install SlackerNews with the Helm CLI.
Onboard
Complete the tasks in this section to onboard your application to the Replicated Platform. When you are done, you can continue to the Next Steps to integrate other Replicated features with your application.
Task 1: Create An Application
To get started with onboarding, first create a new application. This will be the official Vendor Portal application used by your team to create and promote both internal and customer-facing releases.
To create an application:
-
Create a new application using the Replicated CLI or the Vendor Portal. Use an official name for your application. See Create an Application.
Can I change the application name in the future?
You can change the application name, but you cannot change the application slug.
The Vendor Portal automatically generates and assigns a unique slug for each application based on the application's name. For example, the slug for "Example App" would be
example-app.Application slugs are unique across all of Replicated. This means that, if necessary, the Vendor Portal will append a random word to the end of slug to ensure uniqueness. For example,
example-app-flowers. -
Set the
REPLICATED_APPenvironment variable to the unique slug of the application that you created. This will allow you to interact with the application from the Replicated CLI throughout onboarding. See Set Environment Variables in Installing the Replicated CLI.For example:
export REPLICATED_APP=my-app
Task 2: Add the Replicated SDK to Your Chart
Next, add the Replicated SDK as a dependency of your Helm chart.
The Replicated SDK is a Helm chart that can be installed as a small service alongside your application. The SDK provides access to key Replicated functionality, including an in-cluster API and automatic access to insights and operational telemetry for instances running in customer environments. For more information, see About the Replicated SDK.
To add the Replicated SDK:
-
In your application Helm chart
Chart.yamlfile, add the YAML below to declare the SDK as a dependency.If your application is installed as multiple charts, declare the SDK as a dependency of the chart that customers install first. Do not declare the SDK in more than one chart. For more information, see Package a Helm Chart for a Release.
# Chart.yaml
dependencies:
- name: replicated
repository: oci://registry.replicated.com/library
version: 1.12.1For the latest version information for the Replicated SDK, see the replicated-sdk repository in GitHub.
Task 3: Configure Your Chart to Use the Replicated Proxy Registry
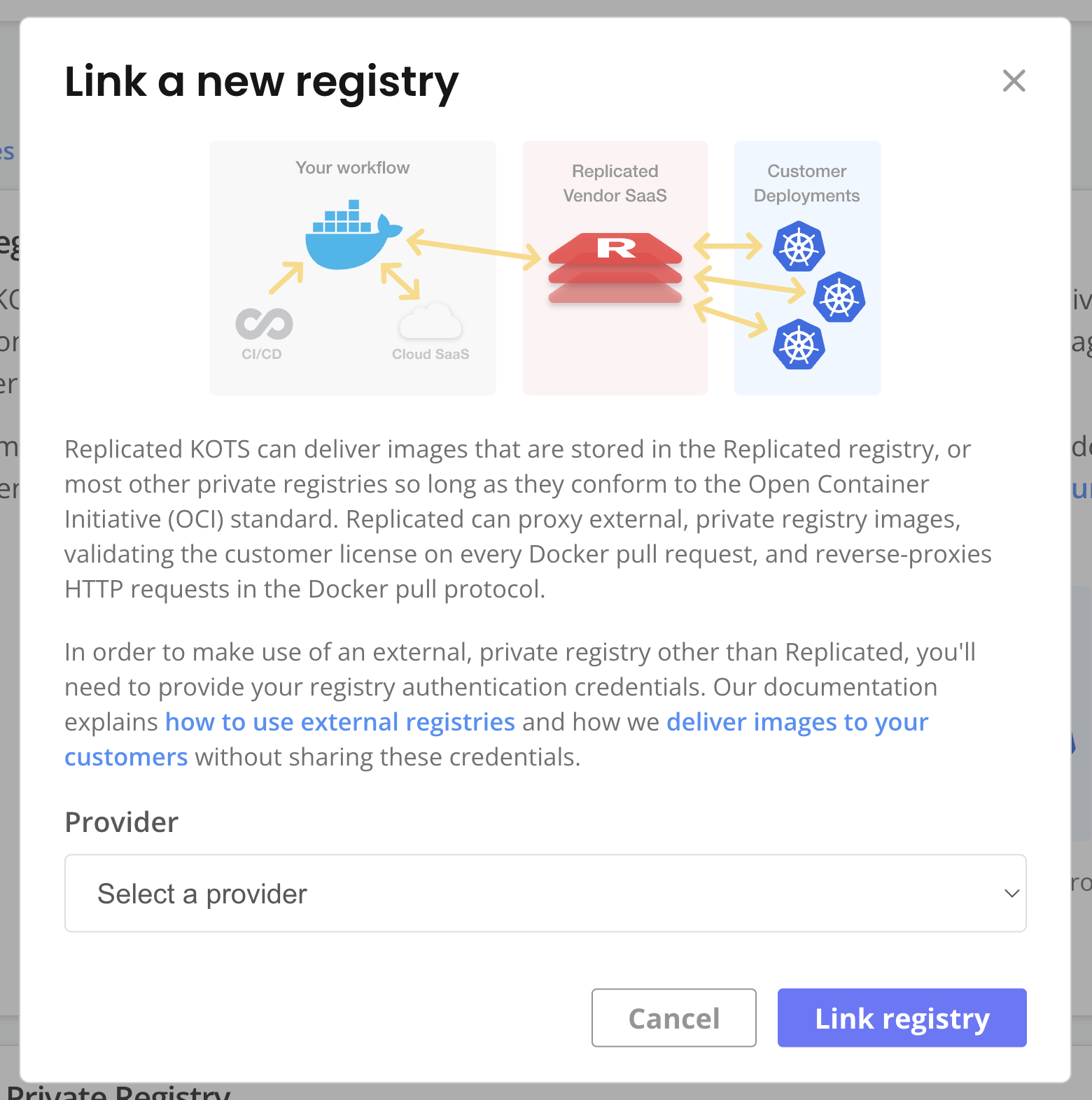
The Replicated proxy regsitry allows you to grant proxy access to your application images without exposing registry credentials to your customers.
To use the proxy registry in Helm CLI installations, update your Helm values so that image references point to the Replicated proxy registry rather than to your default registry. Then, add a Replicated pull secret to your chart to authenticate with the proxy registry. For more information about this process, see Use the Proxy Registry with Helm CLI Installations.
To configure your chart to use the proxy registry:
-
In the Vendor Portal, go to Images > Add external registry and provide read-only credentials for your registry. This allows Replicated to access the images through the proxy registry. See Add Credentials for an External Registry in Connecting to an External Registry.
-
For each image reference in your Helm chart values file, set the image repository URL to the location of the image in the proxy registry.
The proxy registry URL has the following format:
DOMAIN/proxy/APP_SLUG/EXTERNAL_REGISTRY_IMAGE_URLWhere:
DOMAINis eitherproxy.replicated.comor your custom domain.APP_SLUGis the unique slug of your application.EXTERNAL_REGISTRY_IMAGE_URLis the path to the private image on your external registry.
Example:
# values.yaml
api:
image:
# proxy.replicated.com or your custom domain
registry: proxy.replicated.com
repository: proxy/your-app/ghcr.io/cloudnative-pg/cloudnative-pg
tag: catalog-1.24.0Ensure that any references to the image in your Helm chart access the field from your values file.
Example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
containers:
- name: api
# Access the registry, repository, and tag fields from the values file
image: {{ .Values.image.api.registry }}/{{ .Values.image.api.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.api.tag }} -
In your Helm chart templates, add a YAML file that evaluates if the
global.replicated.dockerconfigjsonvalue is set, and then writes the rendered value into a Secret on the cluster, as shown below.Do not use
replicatedfor the name of the image pull secret because the Replicated SDK automatically creates a Secret namedreplicated. Using the same name causes an error.# templates/replicated-pull-secret.yaml
{{- $global := default dict .Values.global -}}
{{- $replicated := default dict (index $global "replicated") -}}
{{- if hasKey $replicated "dockerconfigjson" }}
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
# Note: Do not use "replicated" for the name of the pull secret
name: replicated-pull-secret
type: kubernetes.io/dockerconfigjson
data:
.dockerconfigjson: {{ .Values.global.replicated.dockerconfigjson }}
{{ end }} -
In your
_helper.tpl, add a Helm helper for the image pull secret. This helper creates animagePullSecretsvalue that lists both the Replicated pull secret that you created (if present) as well as any global or chart-level pull secrets provided by your customers. This supports use cases where customers need to provide additional pull secrets, such as in air gap installations where images are pushed to a private regitsry in the air-gapped environment.{{/*
Image pull secrets
*/}}
{{- define "replicated.imagePullSecrets" -}}
{{- $pullSecrets := list }}
{{- with ((.Values.global).imagePullSecrets) -}}
{{- range . -}}
{{- if kindIs "map" . -}}
{{- $pullSecrets = append $pullSecrets .name -}}
{{- else -}}
{{- $pullSecrets = append $pullSecrets . -}}
{{- end }}
{{- end -}}
{{- end -}}
{{/* use image pull secrets provided as values */}}
{{- with .Values.images -}}
{{- range .pullSecrets -}}
{{- if kindIs "map" . -}}
{{- $pullSecrets = append $pullSecrets .name -}}
{{- else -}}
{{- $pullSecrets = append $pullSecrets . -}}
{{- end -}}
{{- end -}}
{{- end -}}
{{/* use secret created with injected docker config */}}
{{- if hasKey ((.Values.global).replicated) "dockerconfigjson" }}
{{- $pullSecrets = append $pullSecrets "replicated-pull-secret" -}}
{{- end -}}
{{- if (not (empty $pullSecrets)) -}}
imagePullSecrets:
{{- range $pullSecrets | uniq }}
- name: {{ . }}
{{- end }}
{{- end }}
{{- end -}} -
Use your helper in any manifests that reference the image.
Example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
spec:
# Add the pull secret with your helper
{{- include "replicated.imagePullSecrets" . | nindent 6 }}
containers:
- name: api
# Access the registry, repository, and tag fields from the values file
image: {{ .Values.images.api.registry }}/{{ .Values.images.api.repository }}:{{ .Values.images.api.tag }} -
If your application is deployed as multiple Helm charts, repeat the previous steps to modify image references and add the pull secret for each of your charts.
-
Update dependencies and package the chart as a
.tgzfile:helm package -u PATH_TO_CHARTWhere:
-uor--dependency-updateis an option for thehelm packagecommand that updates chart dependencies before packaging. For more information, see Helm Package in the Helm documentation.PATH_TO_CHARTis the path to the Helm chart in your local directory. For example,helm package -u ..
The Helm chart, including any dependencies, is packaged and copied to your current directory in a
.tgzfile. The file uses the naming convention:CHART_NAME-VERSION.tgz. For example,postgresql-8.1.2.tgz.noteIf you see a
401 Unauthorizederror message, log out of the Replicated registry by runninghelm registry logout registry.replicated.comand then runhelm package . --dependency-updateagain. -
If your application is deployed as multiple Helm charts, package each chart as a separate
.tgzarchive using thehelm package -u PATH_TO_CHARTcommand.
Task 4: Add the HelmChart Custom Resource and Create a Release
For each Helm chart used by your application, add a unique Replicated HelmChart custom resource. Replicated uses the HelmChart resource to generate a list of the images that are used by your Helm chart. This enables features such as air gap installations and scanning and reporting on application images with the Replicated Security Center (Alpha). For more information, see HelmChart v2.
After you configure the HelmChart custom resource, you can create and promote your first release in the Vendor Portal.
To add one or more HelmChart custom resources and create a release:
-
In the local directory for your application Helm chart, create a subdirectory named
manifests. This is where you will add the files for your release. -
Move the
.tgzchart archive(s) that you packaged in the previous task to themanifestsdirectory. -
In the
manifestsdirectory, create a new YAML file namedYOUR_CHART_NAME.yaml, whereYOUR_CHART_NAMEis the name of your chart. For example,samplechart.yaml. -
In the
YOUR_CHART_NAME.yamlfile, add the following YAML to create a HelmChart custom resource. Update the values forchart.nameandchart.chartVersionto match the name and version of the corresponding Helm chart.# HelmChart custom resource
apiVersion: kots.io/v1beta2
kind: HelmChart
metadata:
name: samplechart
spec:
chart:
# name must match the chart name from the .tgz chart archive
name: samplechart
# chartVersion must match the chart version from the .tgz chart archive
chartVersion: 1.2.3noteFor online (internet-connected) Helm CLI installations, you do not need to configure any additional fields in the HelmChart custom resource besides
chart.nameandchart.chartVersion. If you also plan to support Helm CLI installations in air-gapped environments, you will update the HelmChart custom resource as part of Next Steps > Add Support for Air Gap Installations. -
If your application is deployed as multiple Helm charts, repeat the previous steps to add a unique HelmChart custom resource for each Helm chart archive in the release.
-
From the
manifestsdirectory, use the Replicated CLI to create a release and promote it to the Unstable channel. For more information, Managing Releases with the CLI.replicated release create --yaml-dir . --promote Unstable -
Install the release in a development environment to test. See Install with Helm.
After successfully installing the release in a cluster with the Helm CLI, go to the next task. You will continue to iterate throughout the rest of the onboarding process by creating and promoting new releases, then installing the new version in your development environment.
Task 5: Set Up the Enterprise Portal
The Replicated Enterprise Portal is a customizable, web-based portal where your customers can find installation instructions, check for application updates, manage their team members, upload support bundles, and more. For more information, see About the Enterprise Portal.
To set up the Enterprise Portal:
-
(Recommended) Add a custom domain for the Enterprise Portal. See Use Custom Domains.
noteYou can also do this later as part of Alias Replicated Endpoints With Your Own Domains.
-
Customize Enteprise Portal settings and the customer-facing install and upgrade instructions. See Customize the Enterprise Portal.
-
Enable the Enterprise Portal for an internal development customer so that you can test your changes. For information about how to enable and then access the Enterprise Portal for a customer, see Manage Customer Access to the Enterprise Portal and View a Customer's Enterprise Portal. For information about how end customers can log in to and use the Enterprise Portal, see Log In To and Use the Enterprise Portal.
-
When you are ready, enable the Enterprise Portal so that it is available to one or more of your end customers. You can enable the Enterprise Portal for all customers by default, or manage access on a per-customer basis. For more information, see Manage Customer Access to the Enterprise Portal.
-
(Optional) Enable self-service signups so that current and potential customers can access your application by signing up for a trial or community license through the Enterprise Portal. See Enable Self-Service Sign-Ups.
Task 6: Define Prelight Checks
In the next two tasks, you will add specs for preflight checks and support bundles.
Preflight checks and support bundles are provided by the Troubleshoot open source project, which is maintained by Replicated. Troubleshoot is a kubectl plugin that provides diagnostic tools for Kubernetes applications. For more information, see the open source Troubleshoot documentation.
Preflight checks and support bundles analyze data from customer environments to provide insights that help users to avoid or troubleshoot common issues with an application:
- Preflight checks run before an application is installed to check that the customer environment meets the application requirements.
- Support bundles collect troubleshooting data from customer environments to help users diagnose problems with application deployments.
To define preflight checks for your application:
-
In your Helm chart
templatesdirectory, add a Kubernetes Secret that includes a preflight spec. For more information, see Define Preflight Checks. For examples, see Example Preflight Specs.If your application is deployed as multiple Helm charts, add the Secret to the
templatesdirectory for the chart that is installed first. -
Update dependencies and package the chart as a
.tgz:helm package -u PATH_TO_CHARTWhere:
-uor--dependency-updateis an option for thehelm packagecommand that updates chart dependencies before packaging. For more information, see Helm Package in the Helm documentation.PATH_TO_CHARTis the path to the Helm chart in your local directory. For example,helm package -u ..
The Helm chart, including any dependencies, is packaged and copied to your current directory in a
.tgzfile. The file uses the naming convention:CHART_NAME-VERSION.tgz. For example,postgresql-8.1.2.tgz. -
Move the
.tgzchart archive to themanifestsdirectory. -
Create a new release and promote it to the Unstable channel. For more information, see Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal or Managing Releases with the CLI.
-
Install the release in your development environment to test. See Install with Helm.
-
Continue to create and test new releases with additional preflight checks until you are ready to move on to the next task.
Task 7: Add a Support Bundle Spec
To add the default support bundle spec to your application:
-
In your Helm chart
templatesdirectory, add the following YAML to a Kubernetes Secret to enable the default support bundle spec for your application:apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
labels:
troubleshoot.sh/kind: support-bundle
name: example
stringData:
support-bundle-spec: |
apiVersion: troubleshoot.sh/v1beta2
kind: SupportBundle
metadata:
name: support-bundle
spec:
collectors: []
analyzers: []noteIf your application is installed as multiple Helm charts, you can optionally create separate support bundle specs in each chart. The specs are automatically merged when a support bundle is generated. Alternatively, continue with a single support bundle spec and then optionally revisit how you organize your support bundle specs after you finish onboarding.
-
(Recommended) At a minimum, Replicated recommends that all support bundle specs include the
logscollector. This collects logs from running Pods in the cluster.Example:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Secret
metadata:
name: example
labels:
troubleshoot.sh/kind: support-bundle
stringData:
support-bundle-spec: |-
apiVersion: troubleshoot.sh/v1beta2
kind: SupportBundle
metadata:
name: example
spec:
collectors:
- logs:
selector:
- app.kubernetes.io/name=myapp
namespace: {{ .Release.Namespace }}
limits:
maxAge: 720h
maxLines: 10000For more information, see:
- Adding and Customizing Support Bundles
- Example Support Bundle Specs
- Pod Logs in the Troubleshoot documentation.
-
(Recommended) Ensure that any preflight checks that you added are also included in your support bundle spec. This ensures that support bundles collect at least the same information that is collected when running preflight checks.
-
Update dependencies and package the chart as a
.tgzfile:helm package -u PATH_TO_CHARTWhere:
-uor--dependency-updateis an option for thehelm packagecommand that updates chart dependencies before packaging. For more information, see Helm Package in the Helm documentation.PATH_TO_CHARTis the path to the Helm chart in your local directory. For example,helm package -u ..
The Helm chart, including any dependencies, is packaged and copied to your current directory in a
.tgzfile. The file uses the naming convention:CHART_NAME-VERSION.tgz. For example,postgresql-8.1.2.tgz. -
Move the
.tgzfile to themanifestsdirectory. -
Create a new release and promote it to the Unstable channel. For more information, see Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal or Managing Releases with the CLI.
-
Install the release in your development environment to test. See Install with Helm.
For information about how to generate support bundles, see Generate Support Bundles.
-
(Optional) Customize the support bundle spec by adding additional collectors and analyzers.
Task 8: Alias Replicated Endpoints With Your Own Custom Domains
Your customers are exposed to several Replicated domains by default. Replicated recommends you use custom domains to unify the customer's experience with your brand and simplify security reviews. For more information, see About Custom Domains.
To add and use custom domains for Replicated endpoints:
-
Add and verify your custom domain(s) in the Vendor Portal. See Add a Custom Domain in the Vendor Portal.
-
If you add a custom domain for the Replicated proxy registry, update any image references in your Helm chart values to point to your custom domain rather than the proxy registry (
proxy.replicated.com).
Next Steps
After completing the main onboarding tasks, Replicated recommends that you also complete the following additional tasks to integrate other Replicated features with your application. You can complete these next recommended tasks in any order and at your own pace.
Add Support for Air Gap Installations
Replicated supports installations in air gap environments with little or no outbound internet access. For Helm CLI installations, users install by following automatically-generated instructions provided in the Enterprise Portal to pull all images and push them to their local image registry.
Replicated recommends that you use Compatibility Matrix (CMX) to create an air-gapped environment for testing your releases. For more information, see Test in Air Gap Environments.
To add support for air gap installations with the Helm CLI:
-
For each Helm chart in your release, configure the corresponding HelmChart custom resource builder key. In the
builderkey, define any Helm values that must be set so that the output ofhelm templateexposes all container images needed to install the chart. This ensures that the Vendor Portal can build the air gap bundle for the release and generate the customer-facing air gap install instructions in the Enterprise Portal.How do I know if I need to configure the
builderkey?When building an air gap bundle, the Vendor Portal templates the Helm charts in a release with
helm templatein order to detect the images that need to be included in the bundle. Images yielded byhelm templateare included in the bundle for the release.For many applications, running
helm templatewith the default values would not yield all the images required to install. In these cases, vendors can pass the additional values in thebuilderkey to ensure that the air gap bundle includes all the necessary images. If the default values in your Helm chart already expose all the images for air gap installations, then you do not need to configure thebuilderkey. -
Create a new release and promote it to the Unstable channel. For more information, see Manage Releases with the Vendor Portal or Managing Releases with the CLI.
-
In the Vendor Portal, go the channel where the release was promoted to build the air gap bundle. Do one of the following:
- If the Automatically create airgap builds for newly promoted releases in this channel setting is enabled on the channel, watch for the build status to complete.
- If automatic air gap builds are not enabled, go to the Release history page for the channel and build the air gap bundle manually.
-
Enable the Helm CLI Air Gap Instructions (Helm CLI only) entitlement for the customer that you will use to test the installation. See Create and Manage Customers.
-
Follow the steps in Install and Update with Helm in Air Gap Environments to test the installation in a development environment.
Add Custom Metrics
In addition to the built-in insights displayed in the Vendor Portal by default (such as uptime and time to install), you can also configure custom metrics to measure instances of your application running in customer environments. Custom metrics can be collected for application instances running in online or air gap environments using the Replicated SDK.
For more information, see Configure Custom Metrics.
Integrate with CI/CD
Replicated recommends that teams integrate the Replicated Platform into their existing develeopment and production CI/CD workflows. This can be useful for automating the processes of creating new releases, promoting releases, and testing releases with the Replicated Compatibility Matrix (CMX).
For more information, see:
Customize Release Channels
By default, the Vendor Portal includes Unstable, Beta, and Stable channels. You can customize the channels in the Vendor Portal based on your application needs.
Consider the following recommendations:
- Use the Stable channel for your primary release cadence. Releases should be promoted to the Stable channel only as frequently as your average customer can consume new releases. Typically, this is no more than monthly. However, this cadence varies depending on the customer base.
- If you have a SaaS product, you might want to create an "Edge" channel where you promote the latest SaaS releases.
- You can consider a "Long Term Support" channel where you promote new releases less frequently and support those releases for longer.
- It can be useful to create channels for each feature branch so that internal teams reviewing a PR can easily get the installation artifacts as well as review the code. You can automate channel creation as part of a pipeline or Makefile.
For more information, see:
Write Your Documentation
Before distributing your application to customers, ensure that your documentation is up-to-date.
For guidance on how to get started with documentation for applications distributed with Replicated, including key considerations, examples, and templates, see Writing Great Documentation for On-Prem Software Distributed with Replicated in the Replicated blog.
Add Support for Replicated Embedded Cluster Installations on a VM
Replicated Embedded Cluster is a UI-based installer that supports installations on VMs or bare metal servers. Embedded Cluster allows you to distribute a Kubernetes cluster and your application together as a single appliance, making it easy for enterprise users to install, update, and manage the application and the cluster in tandem. For more information, see Embedded Cluster Overview.
Teams with the Business or Enterprise pricing plan can modify existing releases to support Embedded Cluster installations; it is not necessary to create and manage separate releases or channels for each installation method. For more information about how to get access to Embedded Cluster, reach out to your Replicated account representative.